
Introduction
Understanding the Role of ERP Systems
The business world today is highly competitive. Every second counts; that’s why managing time effectively is key.
Many businesses turn to technology to make things faster and smoother. A standout for this job is the ERP integration platform.
But what exactly is an ERP system, and why is it so essential?
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a software that combines various business tasks into one unified system. It lets different departments—like finance, human resources, supply chain management (SCM), and customer relationship management (CRM)—work together seamlessly.
An ERP integration platform acts like a centralized hub. It boosts internal communication, improves operational efficiency, and ensures proper data management.
The Importance of a Unified ERP System
In a business, using disconnected systems can pose serious problems. These systems often focus on specific areas, like inventory, payroll, or customer interactions. But if these systems don’t integrate, they can waste time and cause errors.
For example, information entered into one system doesn’t update automatically in another, causing discrepancies and confusion.
To solve these issues, we can use a united ERP integration platform that handles everything in one place. This way, we don’t need to input data into many systems, saving time and ensuring all employees have the same up-to-date information. As a result, decision-making becomes more informed and efficient.
Key Features of an ERP Integration Platform
The primary characteristics of an ERP integration platform entail having modules of different business functions. These often cover:
- Finance and Accounting: Whether it is a simple financial transaction, a budget calculation or an extensive financial report, such a system will always be accurate in real time.
- Human Resources: Simplify handling of employees’ wages or salaries, providing and planning for employees’ benefits.
- Supply Chain Management: Be in charge of stock, purchase, and supply.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Dedicate accumulated data to improving customers’ experiences, monitoring sales endeavors and improving customer relationships through targeted communication and follow-up.
- Manufacturing and Production: Manage the production, product quality, and procurement of products, ensuring high-quality manufacturing operations.
Several of these applications forming a module are built within a unified ERP integration platform, which provides you a comprehensive vision of your company.
These ERP integrations ensure seamless data flow across departments.
Why Transition to a Unified ERP System?
There is always a positive change for any organization when they switch to a new unified ERP integration platform. Here are a few reasons why:
- Enhanced Efficiency: When all functions are integrated into one system, you are able to minimize issues like duplicate data entry and manual reconciliations. This activity simplifies the process, making it less time-consuming and eliminating the probable mistakes.
- Cost Savings: A unified system is more cost-effective because you purchase one software solution instead of acquiring many from various vendors, which would require different licenses for the company to purchase. It also reduces the cost of using IT infrastructure as maintaining one system is more affordable than having many.
- Better Decision-Making: Data is integrated into one system, resulting in real-time analytics and reporting. This mode of managing data also assists in providing business solutions with more precision and at the right time.
- Improved Collaboration: When engaged in the implementation of a unified system, the departments are able to communicate frequently. They are able to share information and thus, work in a better way, solving issues of poor collaboration and project management.
To sum up, the decision to implement an ERP integration platform is a right strategic decision that will certainly result in the increase of business efficiency. Through integration of multiple functions in one, unified system, the aim of defeating the odds of a disjointed software is realized by providing better organizational outcomes.
As the business world goes through its creative journey, proper management of ERP systems will be mandatory for competitiveness.
In this guide, you will learn how to achieve maximum benefit out of an ERP integration platform and how it can revolutionize your business.
The Evolution of ERP Systems
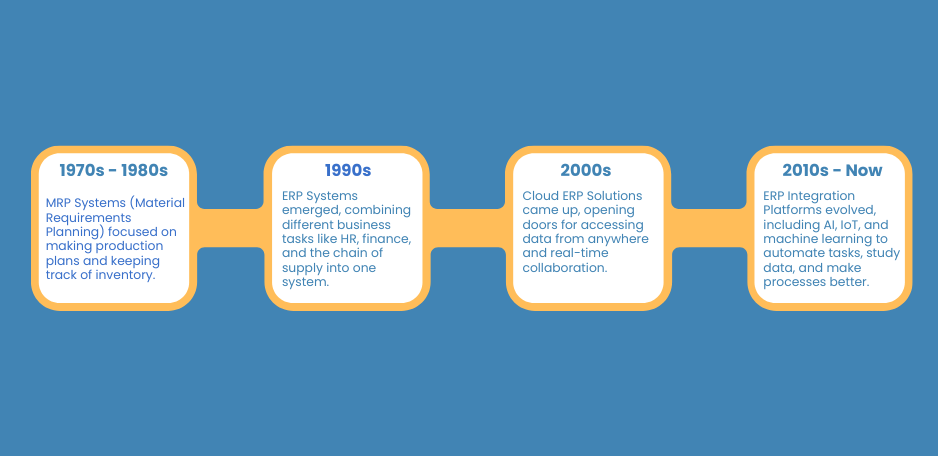
The Early Days of ERP
The history of ERP systems began in the 1960s with the introduction of Inventory Management Systems. These initial systems were primarily concerned with the management of inventory and production schedules. Companies like Ford and Boeing utilized these systems. They aimed to better inventory tracking and improve the management of production schedules.
At this stage, ERP systems were essentially standalone solutions; each designed to handle a single aspect of a company’s operations. Since these systems were not interconnected, businesses had to manually compile data from different sources.
In the 1970s and 1980s, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems emerged. Some of these systems extended to planning and control of production and manufacturing scheduling. However, they remained as standalone modules and did not interact with other areas of business.
The Shift to Integrated ERP Solutions
In the 1990s, the idea of an ERP integration platform started developing. Thus, it was a characteristic epoch in the movement from the individual systems to the integrated ones. This was the period when the term ‘Enterprise Resource Planning’ was coined after society realized that there was the need to develop a single system that was capable of handling most of the key business processes.
Key developments during this time included:
- Integrated Modules: Integrated modules facilitated an organizational activities which includes; financials, human resource, and supply chain which were integrated within the system.
- Client-Server Architecture: This technology enabled organizations to establish the use of networking ERP systems, which allowed users to simultaneously use a single system.
- Database Management: Centralized databases were effectively utilized and ensured real-time data updates, in addition to minimizing duplication.
Modern ERP Systems and Technological Advances
With increase in technology, ERP integration platform systems also advanced into the new millennium and beyond into the 2000s. The emphasis was made on developing new systems that are scalable and more generic, yet easier to utilize. This period saw several notable innovations.
Cloud-Based ERP integration platform
This changed with the rise of cloud computing which was instrumental in changing ERP systems.
Several advantages were associated with the integration of cloud ERP platforms, some of which were inexpensive IT infrastructure, flexibility, and the ability to access off-site.
It also meant that businesses could access their ERP systems from anywhere, thus increasing flexibility and hailing increased collaboration.
Mobile Access
Modern ERP systems have started offering mobility access with the availability of smartphones and tablet elements.
The availability of this feature enabled the employees to access the ERP integration platform while on the move, hence enhancing real-time data entry and decision making.
Enhanced User Interfaces
New generation of ERP systems aimed at enhancing user interface and providing an easy to use interface.
This development was initiated for the purpose to make ERP systems more user-friendly so that a lot of purchase is not made but it is implemented and used.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
The use of advanced analytics and reporting tools which were integrated, gave business entities a better perspective of their operations.
These tools featured big data and machine learning to deliver decisions, act as predictors and provide insights to organizations.
Fragmented vs. Unified ERP Systems
Over the years, companies working with ERP systems have faced the decision of choosing between fragmented and unified ERP systems. Here’s a comparison:
Fragmented Systems
Definition: These are multiple, isolated systems for various areas of the business.
Pros:
- These systems may be more specific to particular requirements.
- These systems can be tailored to suit the required need.
Cons:
- Misconnection of data.
- Data silos that prevent smooth information flow.
- More expenses on maintenance.
- Higher chances of inconsistency.
Unified ERP Systems
Definition: This is a single ERP integration platform where all the business functions are handled in a single system.
Pros:
- Allows for seamless integration of data.
- Makes the processes smoother and more cohesive.
- Requires less IT investments and maintenance.
- Ensures more accurate data and better cooperation.
Cons:
- Higher costs at initial stage as compared to other conventional IT applications.
- May require customization for specific business needs.
Technological Advancements Shaping the Future of ERP integration platform
Looking ahead, several technological trends are expected to further shape the evolution of a ERP integration platform:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: It can also be seen that in the context of ERP systems, AI and machine learning are also integrated allowing for more improved analytical, automation, and decision support. These technologies can be applied to analyze the patterns that give some idea about bringing changes in existing processes and getting better results in future.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Integrating an ERP integration platform with IoT enables real-time data collection and processing. This capability is especially helpful for sectors such as manufacturing and logistics; equipment and sensors in these fields collect data in real-time. For instance, GE uses IoT gadgets to keep a watch on machine operations and foresee when upkeep is needed.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is used to collect information by ensuring the ownership of the data by the users with complete security as well as transparency. The connection of the blockchain with the ERP system could potentially lead to an enhancement of the supply chain’s transparency and a decrease in fraud rates combined with an enhancement of the data’s reliability. For instance, Walmart uses blockchain to trace the supply chain of food products, improving food safety.
- Enhanced Integration Capabilities: The future versions of ERP applications shall incorporate these integration strengths and come up with even more integrated systems with other applications, third parties service and data from other external sources.
The Role of Cloud-Based and Hybrid ERP Solutions
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, cloud-based and hybrid ERP solutions are gaining prominence:
- Cloud-Based ERP integration platform:
- Definition: Network-based systems such as those carried out on servers that are accessed through the internet.
- Benefits: By adopting cloud computing, businesses are able to incur relatively low initial expenses, accommodate the scaling needs of the consumers, work remotely, and benefit from automatic updates. For example, Oracle NetSuite provides online ERP solutions. These tools let companies handle financial matters and tasks from any place with internet connectivity.
- Challenges: Issues related to protection of data and vulnerability of internet-dependent systems. For example, businesses must tackle cybersecurity issues to secure sensitive data held on the cloud.
- Hybrid ERP integration platform:
- Definition: A blend of the traditional and the advanced with regards to ERP implementation.
- Benefits: The ability to decide which functions should go to the cloud and which ones should remain inside a company’s infrastructure; suitable for those companies that have particular regulatory or operational requirements. For example, a business may utilize a cloud-based ERP system for handling customer relations. Yet, they keep financial data on-site to follow local rules.
- Challenges: Issues in managing and integrating both on-premises and cloud-based components.
It is important to understand that ERP systems have been through a journey of development and what used to be simple applications for tracking inventory, has developed into fully fledged integrated systems. ERP integration platforms have created dynamic business improvements by changing the mode of operations, increasing the accuracy of business data and improving the decision-making process.
With the growth of technology, the future versions of ERP will be more and more efficient and will present more and more possibilities of integration, thus leading to more and more success for the organizations.
By analyzing this evolution businesses will be able to understand the importance of implementing a contemporary ERP integration platform and get ready for the future of ERP.
Key Features of a Unified ERP System
ERP integration platform or commonly known as a unified ERP system refers to a fundamental system of many current business organizations because of its ability to coordinate multiple operational activities under one comprehensive structure.
This integration tends to make all departments in an organization share the same data, procedures and hence, leads to improvement in efficiency, accuracy as well as improved collaboration.
Here are the details of the most crucial elements that characterize a unified ERP integration platform that is crucial in any business.
Core Functionalities
The key functionalities of a unified ERP integration platform contains several key business processes, all of which revolve around optimizing organizational activities to make them more efficient.
Key modules typically include:
- Finance and Accounting:
- General Ledger: It is involved in centralizing financial transactions as well as, budgeting and preparation of financial statements.
- Accounts Payable and Receivable: It entails the automation of invoice management, payments and customer billing.
- Fixed Asset Management: Accomplishes tracking and maintenance of the company assets as well as depreciation.
- Financial Reporting: Delivers accurate financial information in real-time and allows users to receive any kind of reports.
- Human Resources:
- Employee Management: Responsible for the recruitment, hiring of employees and keeping track of the employees records.
- Payroll: Calculates salaries, deductions such as tax, preparing statements of benefits among other tasks that relate to payroll processing.
- Performance Management: Documents the performance of employees, their aims and achievements.
- Training and Development: Responsible for employee’s education and growth in their career.
- Supply Chain Management:
- Inventory Management: Manages the purchasing of stocks, oversees the stocks and orders new stocks when they run out.
- Procurement: Managing suppliers and procurement for orders so as to automate the purchase order.
- Logistics and Distribution: Manages warehousing, transportation, and distribution of goods.
- Demand Planning: Forecasts demands in order to better control inventory to avoid situations where they run out of stocks or conversely when they end up with excess stocks.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Sales Management: Tracks sales activities, manages leads, and oversees the sales pipeline.
- Customer Service: Answers customers’ queries, assists with concerns, and manages service tickets.
- Marketing Automation: Helps in the automation of marketing communication activities, lead generation and customer segmentation.
- Customer Analytics: Gives an understanding of the customer’s behavior, their behavior, and trends.
- Manufacturing and Production:
- Production Planning: Is in charge with schedule and planning of production runs, work orders, and the monitoring of production tracking.
- Quality Control: Supervises the quality of products developed by the company, oversees inspections and solves quality problems.
- Maintenance Management: Responsible for maintenance schedules, and implements ways of analyzing the performance of equipment.
Customizability and Scalability
One of the most important benefits of a single ERP integration platform is that you can easily tailor the system to meet the requirements of your business and vice versa expand as the business grows. This flexibility includes:
- Customizable Modules: It is also possible to customize specific modules to correspond to the company’s needs and workflow. For instance, a firm may locate adaptation within the particular CRM module where it might add industry-specific functions or processes.
- Scalability: Having a single ERP integration platform for an enterprise resource planning means that the business can scale up as well. The system can grow horizontally by adding new markets or products whilst vertically by adding more users to the system without need of a total redesign.
- Integration with Other Systems: Most of the current ERP integration platforms provide API and integration features to enable them to share data with other software systems, third-party applications, industry-specific tools, and legacy systems.
Data Centralization and Real-Time Access
An ERP integration platform provides the core and consolidates data of different departments into one point of reference. This centralization offers several benefits:
- Single Source of Truth: With consolidation of data into one system, it implies that all the departments of the business will be working on the same information. This eliminates redundancy and stops data duplication, hence ensuring that data sets in the organization are coherent.
- Real-Time Data Updates: This means that when a certain enterprise is implementing its unified ERP integration platform, data is updated in real-time This real-time access to correct information eradicates unnecessary delay in decision making processes and also eliminates the effects of wrong data that may contain errors as compared to current data.
- Comprehensive Reporting and Analytics: Integrated system offers more reporting and analysis features, helping businesses to develop reports, monitor key performance indicators and gather important information about the company.
User-Friendly Interface and Accessibility
The ability to leverage the implementation of a single ERP integration platform is critical in its usability for the employees. Key aspects include:
- Intuitive Interface: Contemporary ERP systems have created user interfaces and interfaces that are easy for the employees to access and work on. This makes it easy for the new users to overcome the initial steep slope and this enhances the utilization of the system.
- Role-Based Access: This means that depending on the user role, availability of the data and the functionalities can be restricted. This makes it possible to limit the information and tools which are available to the employees in order to boost security and productivity.
- Mobile Access: Almost all ERP systems today are compatible within mobile platforms whereby employees can use their phones or tablets. This feature enables the functionality for remote working as well as field operations – which is convenient.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
A unified ERP integration platform can integrate with various emerging technologies to enhance its capabilities:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): ERP system integration with AI enables prompt data processing, and forecasting for decision-making. With the help of AI, huge amounts of data can be worked through and analyzed and different solutions can be suggested.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Manufacturing equipment and sensors can also be connected with IoT to the ERP system and they update real-time data. This integration is very valuable in organizations such as manufacturing and logistic companies for keeping track of the performance of their equipment or to manage operations.
- Blockchain: One is that blockchain technology can be applied in increasing the security and openness of data. which includes:
- The capability of enabling secure transactions.
- Being able to trace a given product as being originated from a specific source.
- Ensuring data integrity.
The parameters arising as a consequence of unifying the ERP integration platform are critical to improving business processes. The various features such as the core functionalities, customization, centralization of data, and user friendliness of the software can all contribute in enhancement of increased and improved efficiency as well as accuracy in an organization.
These features help the businesses to manage their processes well, make right decisions and survive in the current world market.
ERP Integration Platform Examples
1. Cloud-Based ERP Integration Platform
Cloud-based ERP platforms give quick, anytime access to data and team collaboration. Perfect for companies with offsite teams or multiple sites.
Key Attributes:
- Internet access anywhere.
- Auto-updates and less IT costs.
- Better safety with cloud encryption.
2. Modular ERP Integration Platform
Modular ERP platforms let companies pick certain functions (like finance, HR) and add them when necessary. This adaptability fits companies wanting to grow gradually.
Key Attributes:
- Choice of modules.
- Expandable with options to add or remove modules.
- Syncs with other company software.
3. Open-Source ERP Integration Platform
Open-source ERP platforms offer lots of personalization and flexibility for special business requirements. Ideal for companies needing custom solutions but having technical knowledge for setup.
Key Attributes:
- Numerous personalization options.
- Can adapt to unique business methods.
- Calls for technical expertise for creation and upkeep.
These cases spotlight the different types of ERP systems businesses can use to boost operations and productivity.
Benefits of ERP Integration
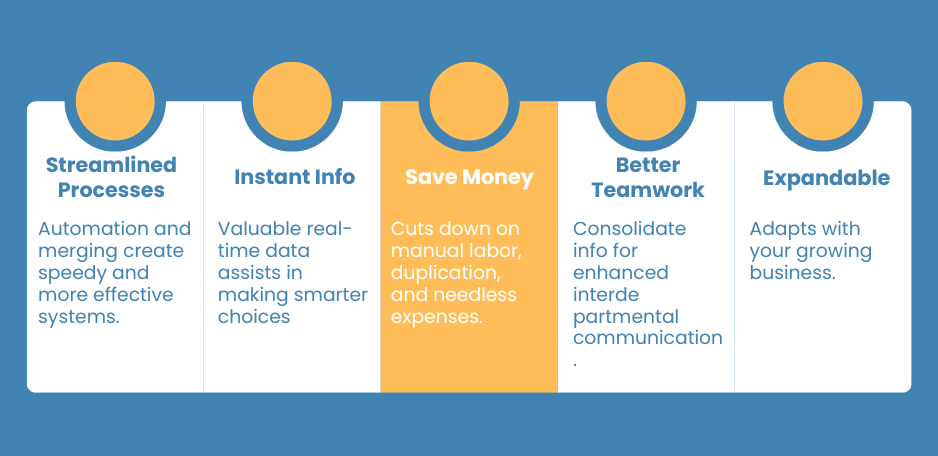
Putting in place a singular ERP system or ERP integration platform can lead to profound improvements for businesses. It merges various internal processes into one collaborative framework, paving the way for better productivity, cost cuts and enhanced decision-making.
Let’s delve into the benefits of transitioning to a single ERP integration platform.
Increased Operational Efficiency
The most significant advantage of adopting a singular ERP integration platform has to do with better operational efficiency. Here’s how it works:
- Reduced Manual Work: Repetitive tasks such as billing, salary calculations, and stock management are taken over by automated features within ERP integrated platform. This means less manual work, fewer mistakes and more time for employees to tackle more impactful tasks.
- Streamlined Processes: By integrating business functions into one system, unnecessary steps are removed, making operations smoother. Such integration diminishes the time and effort needed for jobs like data logging, reporting, and inter-departmental communication.
- Improved Workflow: With all facts and operations within the same hub, employees can swiftly access required information. This convenience provides seamless workflows and faster decision-making, boosting total efficiency.
Cost Savings
One of the major benefits of ERP integration is cost saving. Implementing a unified ERP integrated platform into action can significantly reduce business costs.
- Reduced Software Costs: With one ERP integration platform, you pay for fewer software licenses and upkeep contracts. These savings can be substantial.
- Lower IT Infrastructure Expenses: Taking care of one system is usually more cost-effective than looking after different ones. A unified ERP integration platform needs less IT support and doesn’t demand as much time or effort.
- Decreased Operational Costs: By making processes simple and automating jobs, companies can bring down everyday costs because of less work, fewer mistakes to fix and improved overall efficiency.
Better Decision-Making
With a unified ERP integration platform, you get updated information that helps you make better decisions:
- Real-Time Data Access: With all data in one place and updated instantly, those in charge can see the latest data right away. This immediate access enables more accurate and timely decisions.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting: New ERP integration platform systems have top-grade analysis tools and reporting features. They let firms make thorough reports, track important KPIs, and look at trends to plan strategic moves.
- Enhanced Forecasting: Companies can use past data and trend predictions to guess what might happen next. You can predict customer needs and potential challenges.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
A unified ERP integration platform boosts teamwork and conversation in an organization:
- Centralized Information: Storing all data in one system allows employees from different departments to access the same information. This centralization boosts coordination and helps everyone work with precise, fresh data.
- Enhanced Interdepartmental Communication: Linking different business sectors improves communication among departments.
- Unified Platform for Collaboration: Plenty of ERP systems come with features that help teamwork, like common dashboards, project management aids, and chat channels. These features help workers coordinate more effectively on projects and tasks.
Enhanced Customer Experience
A unified ERP integration platform can greatly enhance customer experience through better handling of customer chats and data:
- Improved Customer Service: Quick access to shared CRM modules allows customer service workers to efficiently find client information, track chats, and solve issues more effectively. All these lead to quick response times and happier customers.
- Personalized Interactions: By checking customer data and buying history, businesses can make their marketing and sales efforts suit individual preferences. Tailored offers and targeted chats lead to a better overall customer experience.
- Streamlined Order Processing: Linking sales and supply chain modules ensures that orders get processed effectively, with accurate tracking and on-time fulfillment. Efficient order fulfillment ensures customers receive their products on time.
Scalability and Flexibility
A unified ERP integration platform brings scalability and adjustability, allowing growth to happen:
- Adaptability to Growth: As businesses grow, the ERP integration platform system can be dialed up. This means more users, transactions, and even new business functions can be added. This scalability ensures that the system continues to support the organization’s needs as it grows.
- Customization Options: Todays’ ERP systems can be styled to fit just right with business requirements or processes. Businesses can tailor the system to their needs, rather than adapting to the system.
- Integration with New Technologies: A unified ERP integration platform may have the ability to add new technology into it, this includes AI, IoT, and blockchain. This adaptability enables businesses to leverage new innovations and stay competitive.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
A unified ERP integration platform helps manage compliance and reduces risks.
- Compliance Management: ERP systems can assist in staying up-to-date with regulations like reporting standards, industry rules, data protection laws etc. Automated tools ensure compliance with regulations, reducing the risk of penalties.
- Risk Reduction: By having everything in one place and automatic processes, businesses can cut down on errors. This eliminates inconsistencies that elevate risk. Advanced data security measures keep everything locked safe from unauthorized access.
The benefits of using a unified ERP integration platform are wide-ranging and compelling. It can boost the effectiveness of operations, save costs, help in better decision-making and upgrade the customer experience.
A singular ERP integration platform centralizes data, automates procedures, and delivers real-time data, making operations smoother, cutting costs and preparing for future expansion. Opting for a unified ERP integration platform can change the way a company works and propels its success.
Leveraging an all-inclusive ERP integration platform provides the tools needed for dealing with the intricacies of today’s business world and achieving their goals.
Overcoming Challenges in ERP Implementation
Implementing a unified ERP integration platform offers major benefits for a company, but it’s not a walk in the park.
To get past these hurdles, careful planning, good communication and a strategic mindset are vital. Advanced ERP tools improve data management and automation.
Here’s an in-depth view of typical implementation problems and strategies to overcome them.
1. Insufficient Planning and Preparation
One big hurdle during the implementation of ERP integration platform is the lack of a solid plan. Without proper planning, businesses run into problems that can disrupt the project.
- Define Clear Objectives: Set specific, measurable goals for the ERP integration platform. Clearly define the objectives you aim to achieve with the ERP integration platform, whether it’s making operations more efficient, boosting data accuracy, or improving reporting functions.
- Conduct a Needs Assessment: Analyze current processes and highlight areas that need upgrading. This analysis assists in choosing an ERP integration platform that fits your business and avoids unneeded features.
- Create a Detailed Implementation Plan: Draft a detailed plan stating the project timeline, resource allocation, and key milestones. Prepare contingency plans ready for dealing with to address any issues that may come up.
Example: A retail company might struggle without proper planning. No precise goals for managing stock could lead to issues. If they set solid targets and carefully evaluate their needs, they can select a good ERP system. They can also make an in-depth plan to guarantee a problem-free setup.
2. Selecting the Right ERP System
Choosing the right ERP integration platform is critical to successful implementation. An unsuitable system can cause issues and inefficiency.
- Evaluate Vendors Thoroughly: Research ERP vendors to find one that suits your business needs. Prefer vendors that understand your industry and have good customer feedback.
- Consider Scalability: Ensure the ERP integration platform can scale with your business. A flexible system provides for future growth, more users, and changing business demands.
- Assess Customization Needs: Ensure the ERP system can be customized to fit your business processes. The ability to adjust the system to your specifics is crucial.
Consider this: A manufacturing company might run into problems if they go for an ERP system that can’t scale with their growth. They could avoid this by evaluating vendors in-depth, thinking about scalability, and ensuring customization options. Doing so, they can select a system that backs their growth and adapts to their processes.
3. Data Migration and Integration
Migrating data to a new ERP platform can be complex and risky. Proper data transfer and integration ensure data integrity and smooth system operations.
- Plan Data Migration Carefully: Build a thorough plan to move data that includes mapping, cleaning, and checking data. Ensure data is accurately transferred using reliable migration tools.
- Perform Data Quality Checks: Clean and validate data before moving it to get rid of duplicates, mistakes, and gaps. High-quality data lets the ERP integration platform function well.
- Test Integration Thoroughly: Check the ERP integration platform’s connectivity with other apps and systems in your company. Ensure data flows seamlessly between systems and that all integrations function as expected.
Example Scenario: Consider a firm that faced some major challenges while migrating data. The issues came from not cleaning the data well enough and insufficient planning. They faced issues like mismatched data and failed integration methods. But, the firm tackled these problems head-on by setting up a clear strategy and using the latest data migration tools. In the end, they successfully resolved these problems, ensuring a smooth transition to their new ERP system.
4. Change Management and User Adoption
Managing change is essential during ERP integration platform implementation. Employees may struggle to adapt to new workflows and tools.
- Communicate the Benefits: Explain to workers the benefits of the new ERP integration platform. Show how their jobs will get better and more efficient.
- Provide Adequate Training: Give full training to users so they understand the new setup. Training should cover all aspects of the ERP platform, including key features and those that match their jobs.
- Address Resistance to Change: Be prepared to address employee resistance to new technology. Include them in the setup process and help them adjust.
Example Scenario: A company faced resistance during their ERP rollout. However, they strategically planned their communication, bringing in key team members during training sessions. These steps helped them tackle issues head-on and showcase the benefits, leading to increased user adoption and minimized disruptions.
5. System Customization and Configuration
Customizing the ERP integration platform to meet business needs can be tough. The right amount of personalization improves system performance.
- Balance Customization and Standardization: Personalization is key, but avoid too many changes that could make future upgrades and upkeep hard. Aim for a balance between personalization and standard features.
- Engage with Experts: Team up with ERP integration platform professionals with experience in personalizing and setting up the system. Their skills can make sure the system matches your requirements.
- Test Customizations Thoroughly: Before finalizing changes, check them thoroughly to make sure they function correctly and integrate well with other system components.
Example Scenario: A business heavily customized their ERP system. This led to problems when updating the software. On the other hand, a different business only made crucial changes but kept most standard features. This led to easier updates and a better performing system overall.
6. Ensuring System Security
Ensuring the security of your ERP integration platform is essential. By doing this, sensitive data stays safe and the system keeps its integrity.
- Implement Robust Security Measures: Implement solid safety protocols, like codes, access controls, and verification processes. Prevent unauthorized access and mitigate potential security threats.
- Regularly Update and Patch: Always keep the ERP integration platform and its software current with new safety patches. Regular updates address vulnerabilities and protect against new threats.
- Conduct Security Audits: Regular safety tests can find and fix potential risks. Work with safety professionals to look over the system’s security situation and make needed changes.
System safety is an ongoing process. Continuous supervision and regular updates are key to upholding a secure ERP environment and shielding sensitive data.
Example Scenario: Consider a company with broken security measures, resulting in a data breach. They tackled this by ensuring consistent updates and frequent security checks. This massively cut down their vulnerabilities, boosting their system’s security.
7. Managing Costs and Budget Constraints
Setting up an ERP integration platform can be pricey. It’s vital to manage costs to stay within budget and make the implementation a success.
- Create a Realistic Budget: Make a detailed budget that includes every cost relating to the ERP integration platform, like licenses for software, hardware, training, and consulting fees. Consider both initial and ongoing costs.
- Monitor Expenses: Monitor costs throughout the ERP implementation process to keep in line with your budget. Address any budget adjustments timely to prevent cost overruns.
- Negotiate with Vendors: Negotiate with ERP vendors to secure a good deal. Look for discounts, service bundles, or flexible payment options.
Example Scenario: Consider a business grappling with budget overruns because of unforeseen costs and lack of financial oversight. They managed to get their budget back on track by keeping a close watch on their expenses and negotiating better terms with vendors. This strategy helped them align their budget again and complete the project successfully.
8. Post-Implementation Support and Maintenance
ERP implementation does not end once the system is up and running. Support and maintenance are key for making sure the system keeps serving the business.
- Establish Support Channels: Establish processes for users to report issues, seek assistance, and receive timely solutions.
- Regular System Reviews: Regular system checks can find how well the ERP integration platform is working and pinpoint ways to make it better. Get feedback from users to learn about their issues and address them.
- Plan for Upgrades: Stay on top of ERP integration platform updates and new features. Schedule regular updates to ensure the system stays efficient.
Continuous support and maintenance are important for the long-term success of an ERP integration system.
Example Scenario: A company overlooked the importance of support after introducing a new system. This led to glitches in operations and unsatisfied users. To resolve this, they set up a round-the-clock help desk. They also started monitoring the network performance on a regular basis, which helped them improve overall system effectiveness.
9. Aligning ERP Implementation with Business Goals
To gain the full benefits of your ERP integration platform, it must align with your business goals.
- Set Clear Objectives: The ERP system needs to match your business strategy and goals. Define how the ERP integration platform will help achieve business goals.
- Measure Success: Lay out key performance Indicators (KPIs) for evaluating the ERP integration platform’s success. Use these KPIs to monitor its impact and proficiency.
Example Scenario: Consider a company that made its ERP system align with its growth plan. This resulted in better operations and satisfied customers. They set clear KPIs, regularly checked the system performance, and made changes when needed. In the end, the ERP system helped them reach their goals.
To overcome ERP integration platform difficulties, careful planning and support are needed. By addressing concerns regarding planning, choosing the system, data transfer, managing change, customization, security, cost and post-deployment support, businesses can effectively use an ERP integration platform for numerous advantages.
Good strategies and support can help businesses handle the complexities of ERP deployment, resulting in an efficient system, better decision making, and business success.
How to Select the Best ERP Integration Platform for Your Business
Selecting the right ERP integration software, or ERP integration platform is vital for perfecting your business processes and attaining operational success.
The numerous options available make the selection challenging.
Here’s a detailed guide to help with the process and choose the best ERP integration platform for your business.
1. Understand Your Business Needs
Picking a suitable ERP integration platform starts with knowing your business needs in depth. Do this by:
- Assessing Current Processes: Check your processes now, spot flaws, and pinpoint parts to make them better. Knowing these issues assists in choosing an ERP integration platform that can tackle specific problems.
- Defining Key Objectives: Decide on your end result with the ERP integration platform. Maybe you want smoother operations, reliable data, or improved reporting. Defined goals will steer your choices.
- Identifying Essential Features: Note down the features your business can’t do without. You might need finance, human resource, supply chain management, CRM, or manufacturing modules.
2. Evaluate ERP Vendors
The right vendor matters as much as the right ERP integration platform. When assessing vendors consider:
- Industry Experience: Opt for vendors having familiarity with your field. They’ll better grasp your unique needs and hurdles.
- Reputation and References: Checkup on vendor reputation and ask for references from others who’ve used their system. Positive feedback and proven success signal reliability.
- Customer Support and Service: Check how the vendor handles customer support and services. They should provide enough help during and after setting up, including training and solving issues.
3. Consider Scalability and Flexibility
A good ERP integration platform needs to adapt and grow with your business. Think about scalability like this:
- Scalability: Choose an ERP integration platform that expands with your business. Keep in mind the number of people using it, how many transactions it can handle, and the chance to add more parts or features if you need them.
- Flexibility: Now, let’s talk about flexibility. You want a system that can adjust to your business’s ever-changing needs. Look for ways to customize it and the ability to work with other systems and technologies.
4. Assess Integration Capabilities
It’s important that the new ERP integration platform works well with your current software applications.
- Compatibility: Make sure your ERP integration software can integrate with current software applications CRM systems, accounting tools, and industry-specific solutions.
- API and Integration Tools: Also, find out if the ERP integration platform has APIs or integration tools. These help to move data between systems, this ensures seamless connectivity and data flow.
5. Evaluate User Experience and Usability
User experience and usability of the ERP integration platform matter a lot because they affect how quickly your team adopts the new system and how effective it is.
- User Interface: Pick an ERP integration platform that’s easy to use. A well-designed interface makes it easier to move around and learn the new system.
- Customization Options: Examine how the system can be adjusted to work with your specific workflows and business processes. Things like customizable dashboards, reports, and features make the system more usable and relevant.
6. Consider Total Cost of Ownership
You must check the overall expenses linked with the ERP integration platform, not just the first buying cost:
- Software Licensing Costs: Check software license costs, including any repeated charges for upgrades or more users.
- Implementation Costs: Think about expenses for setting up the system like fees for consultancy, moving data, and customizing.
- Maintenance and Support Costs: Factor in the ongoing costs for maintenance and support, which could include updates, tech assistance, and training.
7. Review Security Features
Keeping data safe is vital for any ERP integration platform. Make sure the system has strong safety measures to protect important data:
- Access Controls: The ERP integration platform should have powerful user limits so that only approved users can get specific data and functions.
- Data Encryption: Look for data encryption features that protect data while it’s being moved and when it’s stored. This stops unapproved access and data leaks.
- Compliance: Make sure the ERP integration platform sticks to necessary data protection rules and industry standards.
8. Evaluate Implementation and Training Support
Good setup and training are vital for a good ERP rollout:
- Implementation Support: Choose a vendor that gives full setup help, including managing the project, configuring the system, and moving data.
- Training Programs: Check the provider’s training offerings to make sure they cover all parts of the ERP system. Training should be given for different user roles and include ongoing help.
9. Test the System Thoroughly
Ensure you examine the entire ERP integration platform comprehensively before making your final decision.
- Demo and Trial: Ask for a demonstration of the system or a trial period. This way, you can use it firsthand. Such experience provides an overview of the system’s capabilities and shows how well it aligns with your needs.
- Proof of Concept: Conduct a proof of concept (POC) to test the system in a real-world scenario. Doing so reveals problems and confirms if the system meets your organization’s needs.
10. Plan for Future Upgrades
Plan for future updates and enhancements to the ERP integration platform.
- Upgrade Path: Familiarize yourself with the vendor’s process for installing new features or delivering new versions. Ensure upgrades cause minimal disruption to daily operations.
- Future Needs: Anticipate future business requirements. Consider how the ERP integration system can evolve to meet future business and technology needs.
Preparing for future changes and improvements keeps your ERP system strong and flexible. Knowing what your business might need and understanding your vendor’s upgrade process can keep your system valuable and working well for a long time.
Choosing an ERP integration platform is a critical choice and it can truly shape the way your business operates. You should know what your business needs, weigh different vendors, think about future scalability, and usability.
Thorough examination of ERP integration platform systems guarantees a choice that fits your objectives and boosts business operations. The right system simplifies your work, improves decision-making, and gears your organization up for lasting success.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Implementing an ERP Integration Platform
Implementing an integrated ERP system, also known as an ERP integration platform, is a tricky task that can offer major benefits if done right.
Though, there are common pitfalls that companies may encounter during the process. Dodging these pitfalls is key to making sure your ERP launch goes well.
Here’s a close look at these common pitfalls and ways you can steer clear.
1. Not Having Clear Goals and Plans
One of the biggest pitfalls in setting up an ERP integration platform is not having clear goals and plans.
- Set Goals: Clearly define what you want the ERP integration platform to achieve. Your goals might include increased efficiency, reduced costs, or enhanced reporting capabilities. Without clear targets, the setup process can lack direction and focus. Set specific, measurable objectives—for instance, aim to cut operational costs by 10% in half a year.
- Make an In-Depth Plan: Draw up a detailed project plan that shows the ERP integration platform’s setup timeline, resources, and key goals met. A detailed plan can help manage expectations and track progress.
Practical Tip: Use tools such as Trello or Asana for project management. These help monitor progress and guarantee that critical steps are achieved promptly.
2. Inadequate Requirement Analysis
Not carrying out a proper needs analysis may result in selecting an ERP platform that does not align with your business requirements.
- Assess Needs: Look at your current procedures and pinpoint what functions the ERP integration platform needs to cover. Talk to stakeholders from all departments to gather feedback on their requirements.
- Rank Needs: Prioritize your needs to ensure the most important ones are addressed first. This aids in giving attention to key features and avoiding unnecessary complications in the ERP integration platform.
Practical Tip: Set up brainstorming meetings or workshop sessions with decision-makers. Do this to fully understand and write down all functional demands before choosing an ERP system. This action makes certain the ultimate solution caters to every department’s demands.
3. Choosing the Wrong ERP System
Choosing an unfit ERP integration platform can hugely affect implementation success.
- Weigh Vendors: Explore and analyze multiple ERP vendors to discover the one that best fits your company’s specific demands. Remember to look into the vendor’s background in your industry, their system abilities, scalability, tailoring possibilities, and the quality of their customer care. A provider with a past success in your field could offer important input and specialized answers.
- Test Well: Don’t settle until you’ve thoroughly tested and made sure the ERP system satisfies your operational needs and fits well with your currently installed systems. Testing can help catch troublesome areas early and reassures you that the selected system will work efficiently within your unique business context.
Practical Tip: Use a vendor scorecard to weigh up ERP choices. Consider aspects such as functionality, how they can grow with you, and the support they offer. Using this method gives you a balanced and well-thought-out result.
4. Poor Data Migration
Data migration is vital when setting up an ERP integration platform. If you don’t manage it well, you could get errors and operational setbacks, which slows everything down.
- Plan Tactically: Build an exact migration roadmap which maps, cleans, and double-checks data. Make sure old data cleanly shifts to the new ERP integration platform.
- Check Data: Ensure all data is accurate and complete before the migration. Resolve data issues before migration to prevent disruptions during implementation.
Practical Tip: Try a test run migration with some of your data; it could flag any issues early on. You can then tackle these head-on before you move everything over, lowering any downtime chances during the full migration.
5. Insufficient Training and Support
Little to no training or assistance can slow down user learning and the system’s power.
- Training for All: Train every user according to their roles. Show them the main features of the ERP integration platform and how it can benefit their daily work. Good training can boost confidence, encourage usage, and improve output.
- Aid Ready: Set up support channels for round-the-clock help, covering the setup and ongoing use. Options can include help desks, webinars, manuals, and dedicated teams. With immediate support, issues get fixed fast to avoid work disruptions.
Practical Tip: Regularly give refresher courses or online courses on new updates. This proactive approach makes sure continuous effective use of the ERP platform.
6. Ignoring Change Management
When change is avoided, employees may resist, harming the ERP integration platform’s success.
- Share Benefits: Outline how the new ERP system will help the workers. It will simplify their duties and boost their efficiency. If workers get how this will make their jobs better, they’ll likely go for it.
- Pull In Employees: Get employees involved in setting up the process. Hear their concerns and clarify how their job will look with the new system. Getting them involved early builds their trust, which helps lessen resistance.
Practical Tip: Launch a well-designed plan for managing change. Regular updates, chance for feedback, and training for staff should be included. This hands-on plan will help handle resistance and get everyone on board.
7. Over-Customization
Too much customization of the ERP integration platform can cause system issues and tricky upkeep.
- Moderate Customizing: Adapting the system to meet specific requirements is good, but going overboard can make future changes harder, raise expenses and draw out the time to get things running. Prime your platform to be both adaptable and capable of ongoing upgrades.
- Standard Features: Trying to use the standard features of the ERP system as much as you can is a smart move. It helps keep things straightforward, cuts down on interruptions during updates, and promotes long-lasting stability.
Consequences of Over-Customization:
- Pricey Updates: Major adjustments usually need more resources for upgrades, as unique setups might not blend well with fresh versions.
- Troubleshooting Troubles: Systems that are overly customized can be hard to fix, straying from the creator’s blueprint.
- Scalability Issues: Meeting future business needs might get harder as too much customizing can limit the ERP system’s adaptability.
Practical Tip: Talk to your vendor before making changes. Their advice could guide you to adjustments that won’t hinder future updates and maintenance.
8. Inadequate Testing
Skipping tests on the ERP integration platform can cause problems. This might lead to system breakdowns and work interruptions. Therefore, testing extensively before using the ERP platform is crucial. This needs to cover:
- Conduct Extensive Testing: Before launching the ERP platform, perform comprehensive testing to identify and resolve any glitches. This should include:
- Functional Testing: It checks that all features of the ERP system are working right.
- Integration Testing: It makes sure that the ERP system links well with your other business tools.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): It involves real users to check that the ERP system suits their needs and works as it should in real-world situations.
- Perform Pilot Runs: A good way to test it is to use the system in a safe zone, often known as a sandbox, or by doing pilot runs. This lets you check how the system works and fix problems before using it fully.
Risks of Skipping Testing:
- System failures can occur from unseen bugs, causing disturbances when the system is live.
- Operational inefficiencies can happen if you don’t test properly as glitches can slow down work, leading to inefficiency and higher costs.
Practical Tip: Always include main stakeholders in UAT to ensure the system works well for the end users. This lowers the chance of problems after the launch.
9. Neglecting Integration Needs
Overlooking integration needs may cause data silos and inefficiencies that limit the effectiveness of ERP integration platform.
- Ensure Seamless Integration: Check if your ERP technology is compatible with current apps and software. A well-integrated system promises easy data transfer and workflow among platforms, reducing hindrances and boosting efficiency.
- Utilize Integration Tools: Apply APIs or resources from your ERP supplier to enhance the link between your ERP system and other software. This prevents data from getting cornered and keeps every system working together well.
Common Integration Challenges:
- Data Silos: When systems don’t communicate with each other, data can get stranded, creating inefficiencies.
- Manual Inputs: If the system doesn’t connect well, you might end up doing repetitive tasks like entering the same data in various systems, upping the chances of errors.
Practical Tip: Work with your IT team and the ERP provider to come up with a list of all apps that need to connect with your ERP technology. This promises compatibility and effortless transitions.
10. Overlooking System Security
Keeping your ERP integrated platform safe is vital. Ignoring this can lead to problems like stolen data, unauthorized entry, and legal issues. You need to have strong security in place.
- Security Measures: Your ERP system should have important safety measures like:
- Access control: Limit who can see key information based on what their job is.
- Encryption: Keep data safe whether it’s being stored or transferred using good encryption.
- Authentication: Use multi-factor authentication, or MFA, to check that someone is who they say they are before letting them in.
- Keep it Current: Regularly update your ERP integration platform and any software linked to it with the newest security patches. This shields your system from new threats.
Why It Matters:
The 2020 security mishap involving SolarWinds’ ERP system signals the serious damage weak security can cause. Data loss and expensive recovery efforts are major concerns.
Legal and Reputational Consequences:
If a company neglects to protect the crucial business and client data, it faces hefty monetary fines. This can also lead to the loss of customer confidence and permanent harm to its reputation.
Practical Tip: Carry out frequent security checks. This helps to spot weak spots and ensures rules set by the industry are followed.
11. Budget Overruns
ERP launch often costs more than expected. This can strain resources and risk financial health.
- Realistic Budgeting: Develop a detailed budget accounting for all expenses. Don’t forget hidden costs like post-implementation support and software licenses.
- Budget Monitoring: Regularly review spending. Address any budget misalignments fast to avoid price inflation. A budget tracking system might be helpful.
Common Budget Overrun Areas:
- Personalization: Tailoring the ERP system to your needs can escalate costs.
- Training: Not budgeting for adequate training could create surprise expenses.
- Scope Creep: Adding features during the project extends time and cost.
Plan for Contingencies:
Have a contingency fund in your budget for any surprises. This helps the project to progress even if unplanned costs arise.
Growth Implications:
Overspending affects more than current resources. It risks long-term objectives and could force cost-cutting in other areas, impacting business efficacy.
Practical Tip: Use project management tools for better ERP project budget handling. It could help detect budget variances early.
12. Lack of Post-Implementation Support
Post-implementation support is vital. It helps keep your ERP integration platform working smoothly.
- Set Support Plans: Make plans for future support and care of the ERP integration platform. Do regular check-ups, update it, and fix issues that might pop up.
- Gather User Feedback: Ask for thoughts from your users to learn about what they experience and what needs to get better. Use this valuable feedback to tweak performance and tackle issues quickly. Keep up with this feedback to make smarter changes that prevent problems before they arise.
- Engage in Proactive Support: Being ahead of the curve with support can prevent long term difficulties. Make a plan to keep an eye on how the system is doing and add updates. For instance, have a review every month to catch any issues early on and deal with them.
Practical Tip: Use a system for tracking user-reported problems. This way, you can track, prioritize, and tackle problems in an ordered way, ensuring you don’t miss anything and handle issues promptly.
13. Misalignment with Business Processes
If your ERP integration platform doesn’t fit well with your business activities, it can cause issues.
- Make Sure System Fits Your Processes: Make sure your ERP integration platform matches well with your company’s tasks and processes. Adapt it to meet your specific needs. Shape its modules to support your firm’s operational requirements.
- Check Workflow Impact: Evaluate how the ERP integration platform will alter your in-place processes. Spot needed changes to boost smooth working and integration. Adjust system setups to make tasks quick and avoid repeating steps.
- Long-Term Expenses: A misfit with firm’s processes can increase costs and impact productivity. Spending time to get the system in place can save you from costly inefficiencies and business slowdowns.
Practical Tip: Run a process check-up before and after ERP setup. This spots any loophole or misfit right at the start. It lets you make needed changes to ensure the system efficiently supports your business methods.
14. No Planning for Scalability
If your ERP integration platform can’t grow with your business, it could limit your future growth.
- Plan for Future Growth: Look for an ERP integration platform that’s scalable. Ensure it can accommodate an increasing number of users, business dealings, and duties as your company expands. Check the platform’s capability to manage large business volumes and a growing number of concurrent users.
- Understand Upgrade Plans: Familiarize yourself with the vendor’s upgrade plan and the process of implementing enhancements. Schedule regular updates to keep the tool current and fully operational. Staying ahead helps avoid possible slowdowns and keeps the system in line with your changing requirements.
Practical Tip: Monitor scalability parameters such as business volume and user capacity to assess if the ERP platform can efficiently support your business expansion. This will aid you in making well-informed choices and avert future interruptions.
15. Not Evaluating Vendors Enough
If you don’t evaluate the ERP vendors well, you might have issues with how your system works and the support you get.
- Research Vendors: Conduct a detailed check on ERP vendors. Check their reputation, customer reviews, and experience. Pick those with a strong history of good implementations.
- Seek References: Request feedback from other businesses who have used the vendor’s ERP integration platform. Positive feedback and proven results show you can trust them.
Practical Tip: Make a list for reviewing vendors. Include things like support after purchase, ways to customize, and the ability to grow. This helps you think about all the important points and select a vendor that fits you.
16. Lack of Executive Support
For a successful ERP initiative, having top management on board is vital.
- Winning Executive Approval: It’s key to ensure leaders are fully on board with the ERP plan. This support is essential for securing both financial and human resources and propelling the project. Without it, the initiative might struggle because of inadequate resources or lack of direction.
- Show the Benefits: It’s essential to convey the ERP integration platform‘s worth to the top brass and stakeholders. Highlight how it aligns with the company’s objectives and drives success.
Practical Tip: Present a compelling business case. Then, show the expected benefits, expenses, and profits of the ERP platform. In doing so, business leaders will find your plan persuasive. This strategy aligns projects with the company’s mission and helps gain the needed dedication.
17. Not Addressing Cultural Challenges
The ERP platform integration may be impacted by cultural roadblocks.
- Reviewing the Company Culture: It’s important to consider how the company culture could influence the ERP implementation. Address cultural barriers early to prevent disruption. The ERP system should be lined up with the company’s ethics and ways.
- Encouraging Teamwork: Departmental collaboration will help with a smoother shift and help counter resistance to change. To deploy a unified ERP integration platform successfully, it’s vital to avoid common ERP mishaps.
Practical Tip: Use change management plans offering practical sessions, open conversation pathways, and ways for feedback. Facing cultural obstacles head-on can avoid disruption and boost the ERP adjustment success.
By tackling issues such as planning, requirements analysis, vendor picking, data shift, training, managing change, customization, testing, integration, security, budget, after-implementation help, and scalability, companies can navigate smoothly and capitalize on their ERP integration platform‘s benefits.
With careful strategizing, proper evaluation, and steady backing, firms can conquer difficulties, harness the ERP integration platform to boost efficiency, aid decision-making, and attain long-term victory.
Future Trends in ERP Systems
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning systems, keep on changing. This is because of tech breakthroughs and shifting company needs. To keep up, businesses need to know what’s coming in ERP integration platform trends.
Let’s delve into the key components shaping ERP’s future.
1. Cloud-Based ERP Systems
First up, we have Cloud-Based ERP Systems. The switch to the cloud is a big deal in an ERP integration platform.
- Flexibility and Scalability: A cloud ERP integration platform is flexible and scalable, meaning cloud ERP systems can be adjusted easily as businesses grow. There’s no need for expensive hardware.
- Cost Efficiency: Plus, it’s cost effective. Cloud ERP integration doesn’t need a large initial outlay of money and operates on a pay-as-you-go basis. This makes it pocket-friendly for companies.
- Accessibility: Then there’s accessibility. Cloud ERP integration can be used from anywhere, promoting remote work and helping teams based in different locations.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Next, let’s consider AI and Machine Learning. These two elements are redefining what ERP systems can do.
- Predictive Analytics: AI and ML can evaluate masses of data to provide predictive information. This can help businesses foresee trends, streamline operations, and make knowledgeable choices.
- Automation: AI within an ERP integration platform can automate routine tasks, like data entry. This can make processes more efficient and lower the risk of mistakes.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Lastly, AI can enrich client experiences. AI chatbots and virtual assistants can improve customer service, offering quick answers and tailored assistance.
3. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things)
ERP platforms are teaming up with IoT. This unlocks new ways to gather and study data in real-time.
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT gadgets give live updates on things like stock amounts, how well machines are working, and supply chain doings. Plugging this data into ERP systems leads to better and speedier decisions.
- Enhanced Visibility: IoT adds a new level of transparency. Businesses can now watch over assets, track shipping, and use resources smarter.
4. Advanced Data Analytics
ERP systems are now leaning more on advanced data analytics.
- Big Data Integration: ERP platforms are now diving into big data analytics. This lets businesses handle and analyze vast amounts of data from different places. The payoff is a deeper understanding of how the business ticks and how customers act.
- Data Visualization: Today, an ERP integration platform comes with high-tech tools that turn complex data into user-friendly visuals, such as dashboards and interactive reports.
5. Mobile ERP Solutions
The growth in mobile tech is driving more mobile ERP solutions.
- Anywhere Access: Mobile ERP apps give users the freedom to tap into the ERP integration platform from a phone or tablet. This means decisions can be made in real time, even while out and about.
- Better Teamwork: Mobile options make communicating and working together easier for teams. No matter where they are, they can instantly get their hands on essential data and tasks.
6. Enhanced User Experience
Boosting how users interact is a crucial function of future ERP integrations.
- User-Friendly Design: An ERP integration platform in the coming years will likely have more straightforward, easy-to-use interfaces. This will help users move through and use the system better.
- Personal Touch: Dashboards and settings that can be modified will lift the user interaction by adjusting the ERP integration platform to each user’s unique patterns and necessities.
7. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain tech stands ready to affect ERP systems, especially where safe and open transactions are vital.
- Improved Security: Blockchain can offer a safe and unchangeable record for transactions, cutting down fraud risk and maintaining data integrity within the ERP integration platform.
- Better Tracking: Blockchain built-in supply chains increase the ability to track transactions and movements, boosting accountability and minimizing mistakes.
8. Integrated Business Intelligence (BI)
Linking Business Intelligence (BI) is rapidly becoming a staple in the modern ERP integration platform.
- Detailed Analysis: ERP platforms are more and more including BI tools that provide a detailed look at business performance, leading to strategic decision-making.
- In-depth Reports: BI features that are integrated, enable detailed reporting abilities, such as adjustable reports, real-time dashboards, and tendency analysis, giving a more profound comprehension of business data.
9. Automation of Routine Tasks
Automation is a big trend leading towards efficiency in the ERP integration platform.
- Streamlining Processes: ERP systems are adding automation for usual tasks like order processing, billing, and inventory, cutting down manual work and boosting accuracy.
- Flow Automation: High-level flow automation aspects simplify business processes by automating approvals, notifications, and task allotments, improving overall output.
10. Greater Focus on User Training and Adoption
ERP systems are getting smarter. This means a lot of focus is on teaching users how to work with them.
- Better Training Methods: Future ERP platforms will have more ways to learn, like step-by-step tutorials, online classes, and user handbooks. This will help users get used to the new ERP integration platform faster and better.
11. Customization and Personalization
Customizing and creating personal options will always be important in ERP systems.
- Made-to-Order Options: Companies will look for ERP platforms that allow changes to match their needs and industry standards.
- Dashboards Just for You: Future ERP systems will have dashboards that users can change to match their job role and likes.
12. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Mixing new tech with ERP platforms will make the system better.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: VR and AR can be added to ERP systems. They can be used for hands-on training, remote upkeep, and an interactive way to look at data.
- 5G Tech: The introduction of 5G will quicken data transfer and make connections happen in real-time. This will boost how fast an ERP integration platform responds.
13. Enhanced Collaboration Tools
Built into ERP systems, these tools elevate cooperation and conversation.
- Integrated Conversations: ERP systems of the future will pack in tools for communication – think about chat options, video discussions, and project leadership facilitators. This would empower team dialogue.
- Cooperative Work Hubs: Future ERP systems will house better joint effort zones for work teams. This helps in sharing information and leads to more effective decision making and project monitoring, leading to more efficient project management and decision-making.
14. Focus on Sustainability and Social Responsibility
An ERP integration platform’s design is now giving priority to sustainability and societal duty.
- Eco-Friendly ERP Systems: Companies are now tilting towards ERP platforms that back environmental-supporting measures like minimizing resource use, lowering waste, and green practices.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): ERP systems are gearing up to add features for tracking societal impact and holding to ethical norms as part of CSR activities.
15. Enhanced Integration Capabilities
Merging smoothly with other systems and technologies is essential for upcoming ERP systems.
- API and Middleware Solutions: Advanced API and middleware tools will strengthen integration capabilities for ERP systems, making connections with secondary applications and services easier.
- Data Compatibility: The future of ERP systems emphasizes better data compatibility, with smooth data flow across different systems. Expect continuous tech advancements and shifting business necessities to define ERP systems’ future look.
Adapting to these changes will help companies maximize their ERP integration platform‘s capabilities and ensure they stay competitive. Staying updated about cloud-solutions, AI and ML, IoT connections, and top-tier data analytics will enable strategic decisions to improve ERP systems. These advancements can streamline operations and promote growth and efficiency, setting the stage for long-term digital success.
Final Thoughts
Every day, the business world changes. Because of this, it is critical for an ERP system, or an ERP integration platform, to keep up. These platforms have moved from just being tools to help automate tasks to complete business management solutions.
ERP integration platforms are always changing to meet what businesses need. Let’s look at some trends we see in the future with ERP integration platforms:
- Cloud-Based Solutions: ERP systems are now being stored in the cloud. This option helps businesses move faster, spend less, and gives easier access to systems.
- AI and Machine Learning: Adding AI and machine learning to these platforms helps analyze data and do routine tasks faster. It also helps predict future needs which can help businesses plan for the future.
- IoT Integration: Including IoT technology in an ERP integration platform helps collect real-time data. It can improve supply chain management and offer predictive maintenance. This leads to your business operating better and moving faster.
To get the most out of your ERP integration platform, you need to understand these trends and how they apply to your business. This helps drive new ideas, streamline processes, and reach important goals. Staying up to date with these trends will ensure the success of your business now and in the future.
Setting up an effective ERP integration platform takes planning, careful evaluation, and constant support. Avoid making common mistakes, know all the key features, and choose the right system. This will help you get the most out of your ERP integration platform and integrate it seamlessly. This will improve how your entire business performs.
Transform Your Business with Virtelligence
Picking the correct ERP integration platform can keep you ahead of the curve and maximize efficiency.
Looking to discover what an advanced ERP integration platform could offer? Virtelligence stands ready to assist. Our specialty is crafting innovative ERP solutions to fit the distinct needs of your company.
We’ve got a team of professionals to help you select, implement, and get the most out of your ERP integration platform.
Don’t lose the chance to upgrade your business with the latest ERP technologies. Get in touch with Virtelligence now and see how our solutions can improve your operations, decision-making and encourage expansion.
Visit us online, or have a chat with our team to arrange a meeting. It’s a step closer to enhancing your ERP system.
With Virtelligence, you can tap into the full strength of your ERP integration platform and guide your business into a more effective, better future.
FAQs
How Does ERP Improve Efficiency?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems enhance efficiency by:
- Centralizing data: It puts all data from various departments into one spot, which cuts down on repetition and enhances accuracy.
- Automating processes: It makes routine jobs quicker and more error-free.
- Enhancing visibility: ERP gives real-time insights into how a business is doing, which helps make decisions faster.
- Improving collaborations: It also helps departments work better together through a unified system. ERP helps businesses run smoother.
What Is ERP Efficiency?
It’s how much an ERP system boosts a company’s performance.
- This involves less manual work and integrated workflows for better productivity.
- It also involves lower operational costs through automation and improved resource management, timely and accurate data for strategic decisions, and less time spent on administrative tasks, which lets employees focus on important activities.
Efficient ERPs lead to more effective and quick business processes.
What Are the Rules of ERP?
ERP systems usually have certain rules:
- Standardization ensures uniformity, Integration ties different business functions together to improve collaboration.
- Customization is when the ERP system is tailored to meet a business’s needs but keeps its core functionality.
- Data accuracy is key for reliable decision-making information.
- User training is essential to make the most of the system.
Following these rules helps get the most out of ERP systems.
What Is One Key to a Successful ERP Implementation?
One key to a successful ERP implementation is thorough planning.
This includes:
- Defining clear objectives.
- Setting specific ERP system goals.
- Making a detailed plan with timeline s, resources, and milestones.
- Involving key stakeholders from various departments.
Proper planning can manage expectations, minimize risks, and ensure a smooth implementation process.
What Are the 7 Steps for Successful ERP Implementation?
Here are the seven steps to put an ERP system in place effectively.
- First, set your goals. Be clear about what you want from the ERP system.
- Second, put together a project team, which should include key stakeholders and project leaders.
- Third, assess your needs. Think about your business processes and determine what your ERP system needs to do.
- Fourth, pick the right ERP system. It should match your needs and help you reach your goals.
- Fifth, make a project plan. This should detail the steps to implement the system, when it should happen, and who should do it.
- Sixth, put your plan to action. Install the ERP system as planned. This includes moving data over, setting up the system, and teaching users.
- Seventh, watch and adjust. Keep checking on how well the system is working and correct anything that’s not helping you reach your goals.
This step-by-step method increases your chance of successfully putting an ERP system in place.
What Is the Key Success Factor of ERP Implementation?
It’s executive support. Here’s why:
- Resources – having the necessary resources and budget is key.
- Change – effective communication and management of changes in the organization are crucial.
- Adoption – executives are able to get employees on-board with the new system.
Executive support helps to tackle problems and makes switching to the new ERP system easier.
How Do You Measure the Success of an ERP System?
Factors include:
- Goal Fulfillment: Check if the system achieves the objectives outlined in the planning stage.
- ROI Analysis: Look at the monetary returns from ERP versus the costs.
- User Reactions: Seek user opinions to find out if the system is meeting their requirements and hopes.
- Efficiency Boost: Monitor the surge in efficiency, productivity, and accuracy after getting the ERP running.
- System Health: Keep an eye on system stats like uptime, speed, and how well it integrates.
These measures give insight into how the ERP is benefiting your business and show where improvements are needed.
How Can I Make My ERP Better?
For a more efficient ERP system, think about these steps:
- Keep it Current: Regularly update your ERP with the latest features and security fixes. This can enhance its usefulness and solve any existing problems.
- Personalization: Customize the ERP to match your unique business needs. Custom sections and add-ons can make the system more relevant and efficient.
- Training Helps: Offer ongoing training and support to help users get to grips with the ERP system. This can encourage better use and more effective system integration.
- Reliable Data: Uphold top-quality data through strict data input and validation rules. Good data is key for trustworthy reporting and decision-making.
- Streamline Processes: Constantly review and tweak business processes to work with the ERP system. This can improve overall performance.
- Listen to Users: Regularly gather user feedback to find ways to improve. Addressing user issues can better the system’s usability and overall effectiveness.
These steps can help you get the most from your ERP and keep it aligned with your business’s demands.
What Problems Can ERP Solve?
There are several areas where ERP can help solve business problems:
- Data Silos: ERP consolidates data from various departments into a single space, fostering better visibility and teamwork.
- Efficiency: Automation and streamlined processes cut out inefficiencies and reduce manual labor.
- Informed Choices: Real-time data and wide-ranging reporting from ERP offer valuable intelligence for better decision-making.
- Inventory Woes: Responsive inventory data from ERP helps manage stock effectively, optimizing supply and reducing costs.
- Customer Service Boost: CRM within ERP offers a panoramic view of customer relations, enhancing responses and personalizing service.
- Compliance in Check: ERP keeps businesses compliant with regulation due to accurate record-keeping and automated reports, lowering non-compliance risks.
- Scalable: ERP can grow with your business, adapting to growth without significant core system alterations. ERP can therefore help businesses run more smoothly and efficiently.